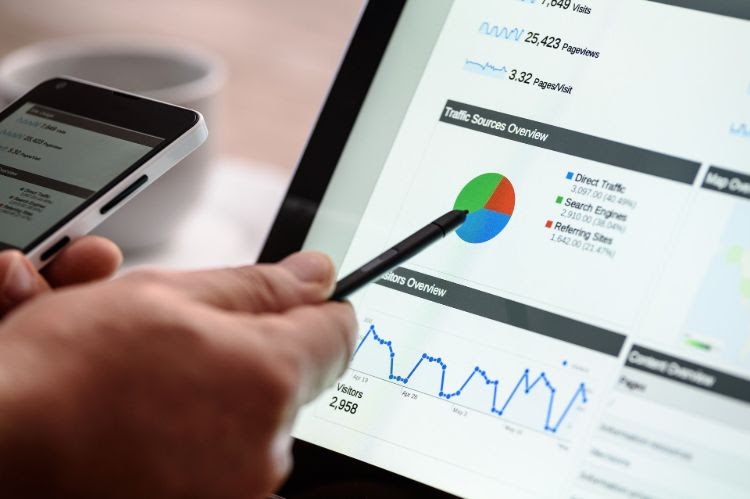
Google’s latest algorithm update indicated it would be user-friendly websites that can provide a superb user experience higher. However, the algorithm update doesn’t indicate the type of web design to use. Herein lies the big question.
Mobile devices come with various screen sizes, which designers must account for during the web design process. Ultimately, web designers can rely on two options to ensure the final web page provides a great user experience, regardless of device. These two options are responsive design and adaptive design.
So, which should you choose between, adaptive vs. responsive design? Here, we’ll compare and contrast both sides of the equation. This way, you can make an informed decision for your eCommerce website.
Responsive Web Design Explained
The term “Responsive Design” comes from career web designer Ethan Marcotte’s book, Responsive Web Design. It describes designs that respond to changes in browser width by tweaking design element placement to fit the current space.
The above implies a responsive website will display content as a function of available space. Say you visit the site with your desktop browser. When you change the browser window’s size, the content on display will move, arranging itself optimally for the new space settings.
The process we describe above happens automatically on a mobile device. The screen size automatically determines the browser width and displays itself in the best arrangement for that screen size.
Adaptive Web Design Defined
An adaptive web design has multiple layout sizes. These layout sizes are fixed and do not change. The earliest mentions of adaptive website design come from Aaron Gustafson’s 2011 book — Adaptive Web Design: Crafting Rich Experiences With Progressive Enhancement.
An adaptive website detects the available browser width and selects the best layout for that screen. It doesn’t always have to be an exact fit. The choice of display layout is often a function of which one is most suitable for the user’s current screen size.
Traditionally, achieving an adaptive web design involves developing layouts for the following screen widths:
- 320 pixels
- 480 pixels
- 760 pixels
- 960 pixels
- 1200 pixels
- 1600 pixels
Adaptive vs. Responsive Web Design: How Do They Compare?
We’ll make it easier to make the right decision by comparing how both web design methods stack up in different playing fields.
Layout
This component is the biggest difference between adaptive and responsive website designs. For the latter, the web page’s layout is dependent on your customer’s browser width.
On the flip side, the choice of layout for an adaptive web page rests with the back end. The system already has a preset choice of layouts unique to different screen devices. The server then uses the device’s OS, model, and screen size to select the right display layout.
Complexity
Certain schools of thought say adaptive designs are more complex and harder to build. After all, building multiple layouts to fit different mobile devices is no mean feat. On the other hand, building a responsive website only requires one display layout.
There may be a layer of truth in the previous paragraph. However, you should also remember that responsive web design requires more upfront investment — time and resources.
Your design team will need to dedicate more time to the ecommerce website’s organization and CSS. The team will need to be agile with the lead person ensuring effective collaborations and guaranteeing results by having proper communication in the work place figuring out how to avoid groupthink.
Ensuring a responsive web design provides the same top-notch user experience regardless of screen size can be an intensive project.
Load Time
We all know the disastrous effects of shopping cart abandonment on your conversion rate. Those cart abandonment numbers may be going up because your checkout page takes too long to load.
A recent report shows that eCommerce conversion rates drop by up to 4.3% for every second the page takes to load. Therefore, how long it’ll take to load personalizing websites should inform your choice between adaptive and responsive design.
Typically, adaptive web pages are the winner in the speed category. The reason is adaptive web pages transfer page elements and assets preset to the native device.
But with advancements in web design technology, that isn’t always the case. Some tools can speed up a responsive web page by building image variants to ensure the site loads quickly, regardless of the device. These web design tools can make your responsive web page’s load time 10x faster.
Adaptability
Adaptive web design is less flexible than a responsive version. Uncommon screen sizes can defeat its foundational multiple layout strategy. Consequently, you’ll need to periodically create new layouts for an adaptive website. You may also have to edit an old web design layout.
Conversely, a responsive web design requires far less maintenance. Even if there’s a new prevalent screen size in the market, a responsive web design will adapt by default. The maintenance needs here are occasional.
Search Engine Optimization
The experts agree that Google favors websites with a responsive mobile design. With SEO at the top of marketing priorities nowadays, it may be best for your eCommerce brand to go with a responsive design.
Adaptive vs. Responsive Design: The Pros and Cons
Sometimes, the best way to decide between two choices is the old-fashioned route. And that route is the trusty, old, pros and cons list.
For Responsive Website Design
Below are the pros of a responsive website:
- Seamless experience: visitors will get the same, familiar experience even when switching devices.
- Budget-friendly: they are easier to develop, and their implementation is fast. Companies offering website design services in Toronto can organize content in one location and manage the website with fewer maintenance needs.
- Improved indexing and crawling: a web crawler only needs to crawl through the page once instead of reconciling different versions of your website.
Here are the drawbacks to using a responsive web design:
- Slower loading speeds: responsive websites load slowly because they load page information for every device, not just the visitor’s viewing device.
- Poor advert integration: page elements on a responsive website morph and adapt depending on the device. However, ads on that page don’t have the same adaptability.
For Adaptive Website Design
Choosing an adaptive design for your eCommerce website offers the following upsides:
- Targeted experiences: optimizing layout for individual pixel sizes and devices means each website user gets a positive experience.
- Fast load times: the back end only loads the page version the visitor needs. Hence, adaptive pages load faster.
- Advert optimization: you can optimize advertisements on your web pages using user data as a guide.
- Editing: the design team doesn’t have to build new layouts from scratch. They can always edit and record an existing web page layout.
The downsides to adaptive web design are:
- Costly: you’ll need a sizable design team to develop, maintain, and support an adaptive website. Consequently, a website development company in Toronto will charge more for adaptive web projects.
- Labor intensive: creating one involves complicated technicalities.
- Harder to maintain: site maintenance is more hands-on. You may need to update your page layout as screen sizes change.
The Case for Adaptive Web Design
Metrics are important to ecommerce brands. The only way to get these numbers up is by increasing organic traffic and, consequently, generating more conversions.
In a search era where user experience is key, an adaptive web design may be the best route to making your site mobile-friendly. It allows for greater control over the design process, allowing you to develop intentional viewports for different pixel sizes.
The design team starts by designing a low-resolution layout. Then they’ll work their way up, designing up to six different layouts. You can also determine which resolution sizes are a priority by exploring web analytics and selecting the most common sizes that visit your website.
The Case for Responsive Web Design
The latest website design trends show newer ecommerce websites are using responsive designs for their pages. This popularity is partly due to the accessibility of responsive themes available through various content management systems.
It’s always better to use responsive web design for a new project. A new ecommerce website will always need all the SEO help it can get. In the same vein, building a responsive ecommerce website requires far less work.
A responsive website design is fluid and uses percentages to boost this fluidity while scaling. This fluidity can cause a jump while the website is resizing. Similar issues make designing a web page with every possible layout in mind a complex endeavor. We recommend creating a layout that fits mid-resolution sizes and adjusts for other resolutions with media queries.
The Choice Is Yours
The information above indicates you can make a case for either a responsive or an adaptive website design. It all depends on the individual nuances of your ecommerce website.
We’ve compared responsive vs. adaptive web design in plenty of detail. Use it as a guide to help you make the right call. You’ve got this!